Authors: Destiny F. Chau, MD - Arkansas Children’s Hospital/University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR and Meera Gangadharan, MD – McGovern Medical School, UTHealth, Houston
A 17-year-old male adolescent with a history of hypoplastic left heart syndrome and Fontan palliation presents for diagnostic cardiac catheterization due to cyanosis with baseline saturations of 87% on room air. A transthoracic echocardiogram shows adequate right ventricular systolic function with mild tricuspid regurgitation and normal neo-aortic valve function. The hemodynamic catheterization reveals Fontan pressures of 13 mmHg, transpulmonary gradient of 4 mmHg, right ventricular end diastolic pressure of 9 mmHg, and an open Fontan pathway with device occlusion of the fenestration. A focused transthoracic echocardiography saline microbubble contrast study is performed with injections into the right pulmonary artery (PA) and produced the findings below.
L Panel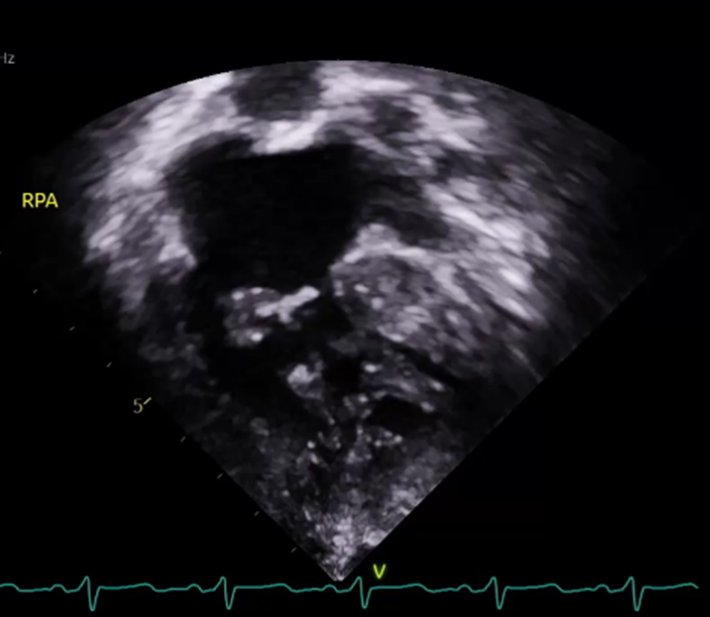
R Panel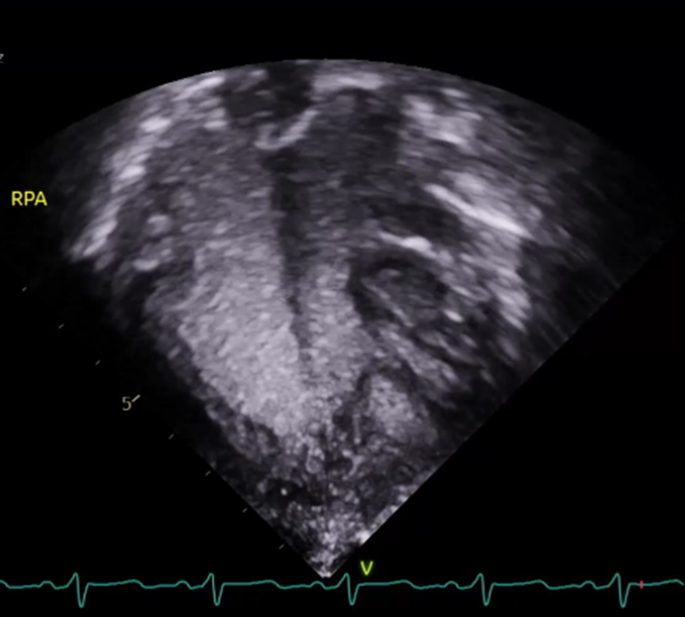 Figure 1. Apical 4 chamber view by transthoracic echocardiogram with saline contrast study. Before (L panel) and after (R panel) saline injection into the right pulmonary artery (RPA). (Image source credit: authors).
Figure 1. Apical 4 chamber view by transthoracic echocardiogram with saline contrast study. Before (L panel) and after (R panel) saline injection into the right pulmonary artery (RPA). (Image source credit: authors).
What is the MOST LIKELY etiology of decreased oxygen saturation?
Correct!
Wrong!
Question of the Week 384